Harry H. Zhang
I am a graduate student in the SPARK Lab of MIT LIDS. I am extremely fortunate to be advised by Prof. Luca Carlone.
Prior to MIT, I was a MS-Research student in the CMU Robotics Institute studying Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, advised by Prof. David Held. I also worked at Amazon as an Applied Scientist II.
Prior to CMU, I earned my B.S. (2017–2021) with Honors from UC Berkeley with a major in EECS and a minor in Mechanical Engineering. During my time at Berkeley, I did research under Prof. Ken Goldberg and Dr. Jeffrey Ichnowski in AUTOLab. I maintain and curate a popular deep reinforcement learning tutorial on my GitHub.
Outside of school, I do quantitative finance.

Research Interests
My current research focuses on trustworthy AI and autonomous systems. Specifically, I design algorithms for machines to learn representations for more robust real-world generalization and better certifiability. My research revolves around the theme of learning-based perception systems and robotic systems.
Research Highlights
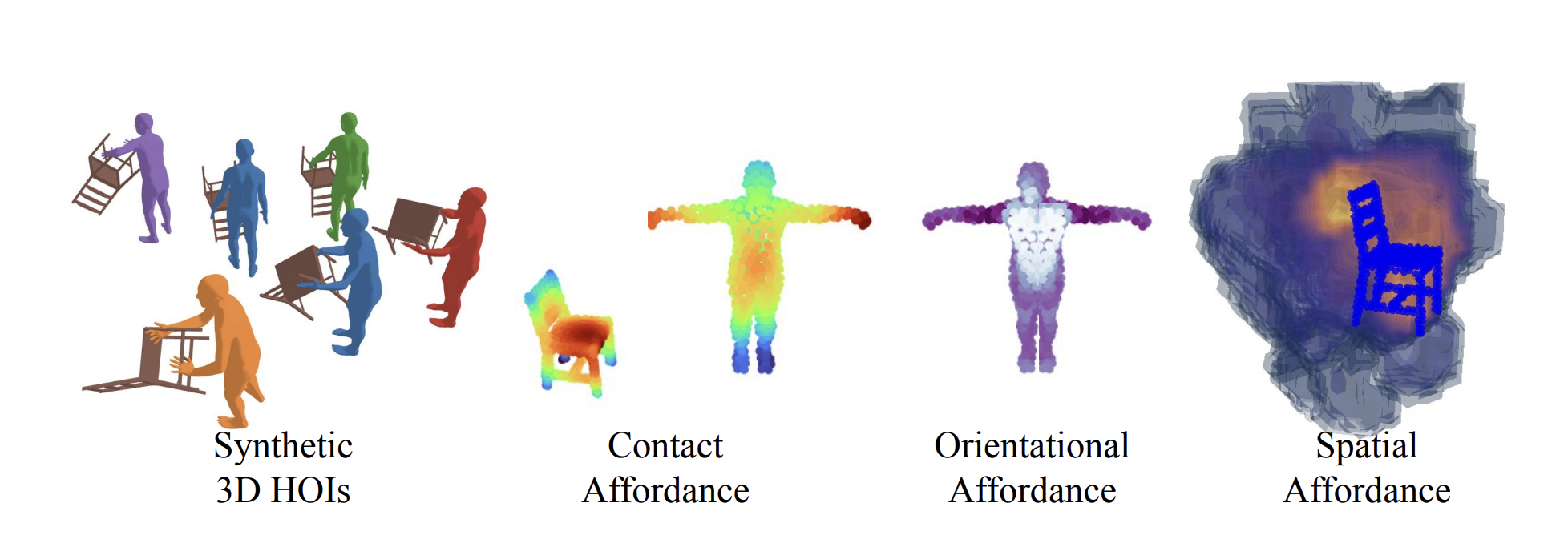
H2OFlow
ICLR 2026
Grounding 3D human-object affordances using generative models and dense diffusion flows.
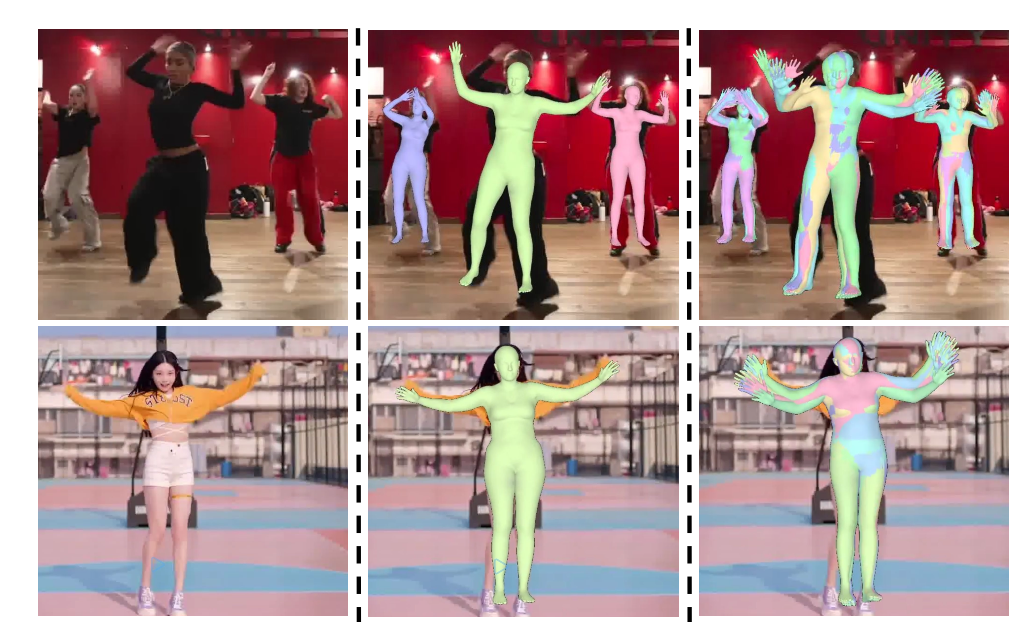

CUPS
ICML 2025
Improving human pose-shape estimation with conformalized deep uncertainty.
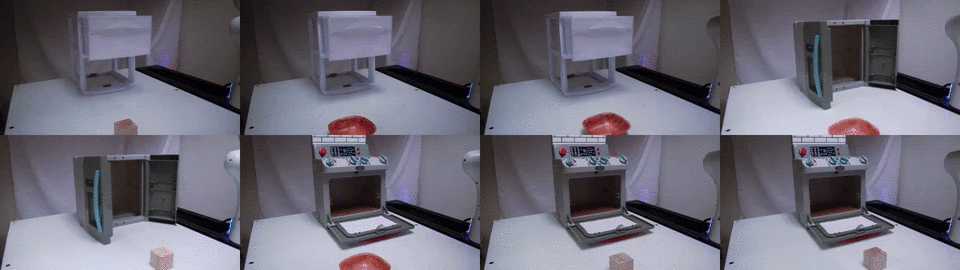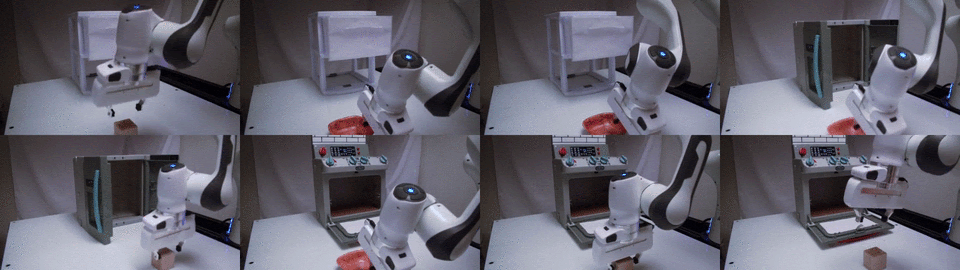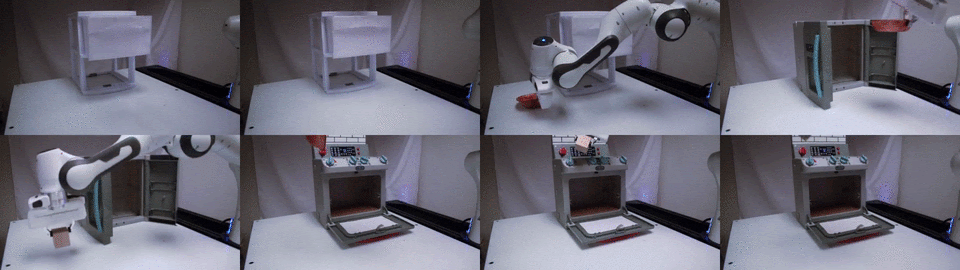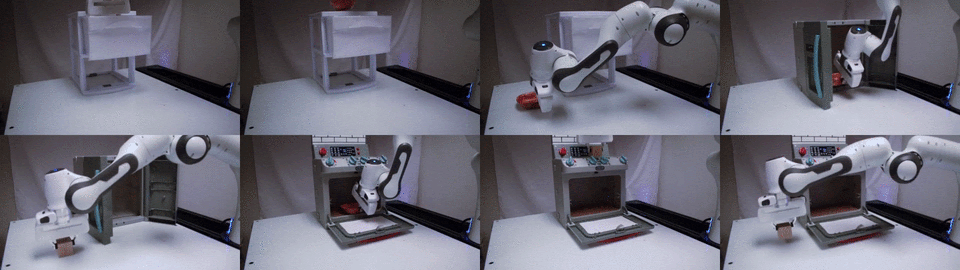
TAX-Pose
CoRL 2022
Task-specific cross-pose estimation for generalizable robot manipulation.

FlowBot3D
RSS 2022 — Best Paper Finalist
Learning 3D articulation flow to manipulate novel articulated objects.