Publications
Peer-reviewed papers and preprints, newest first.
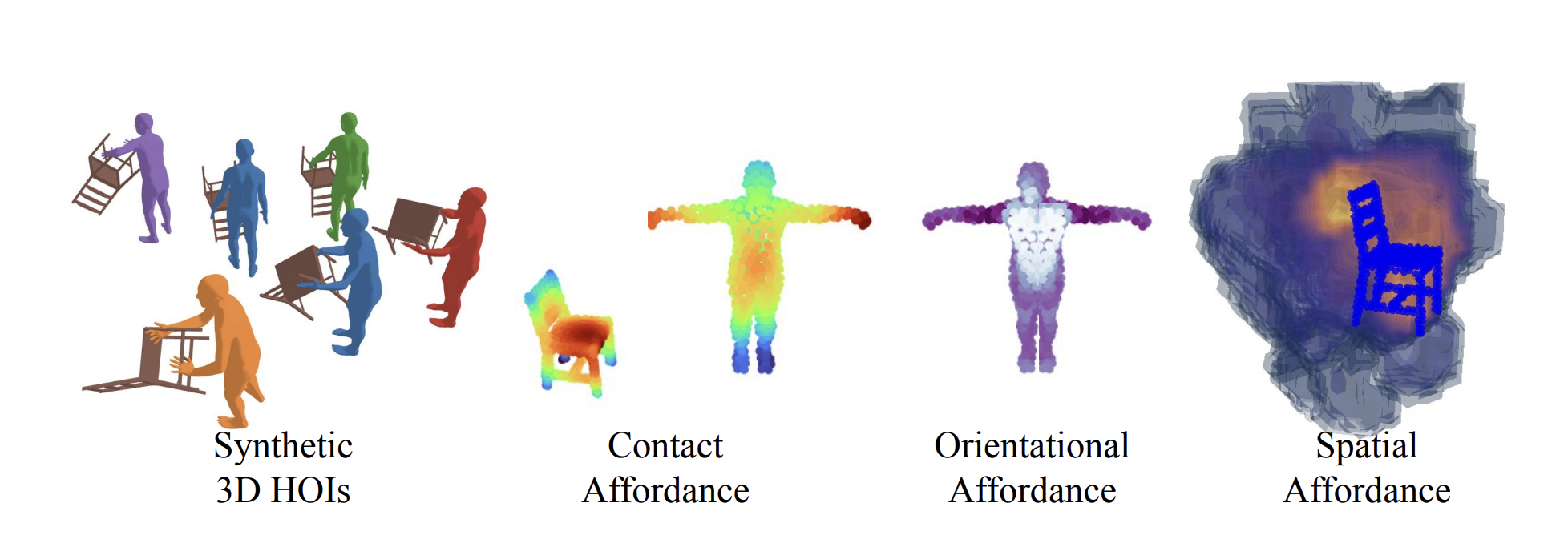
H2OFlow: Grounding Human-Object Affordances with 3D Generative Models and Dense Diffused Flows
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026
We introduce H2OFlow, a novel framework that comprehensively learns 3D HOI affordances — encompassing contact, orientation, and spatial occupancy — using only synthetic data generated from 3D generative models. H2OFlow employs a dense 3D-flow-based representation, learned through a dense diffusion process operating on point clouds. This learned flow enables the discovery of rich 3D affordances without the need for human annotations.
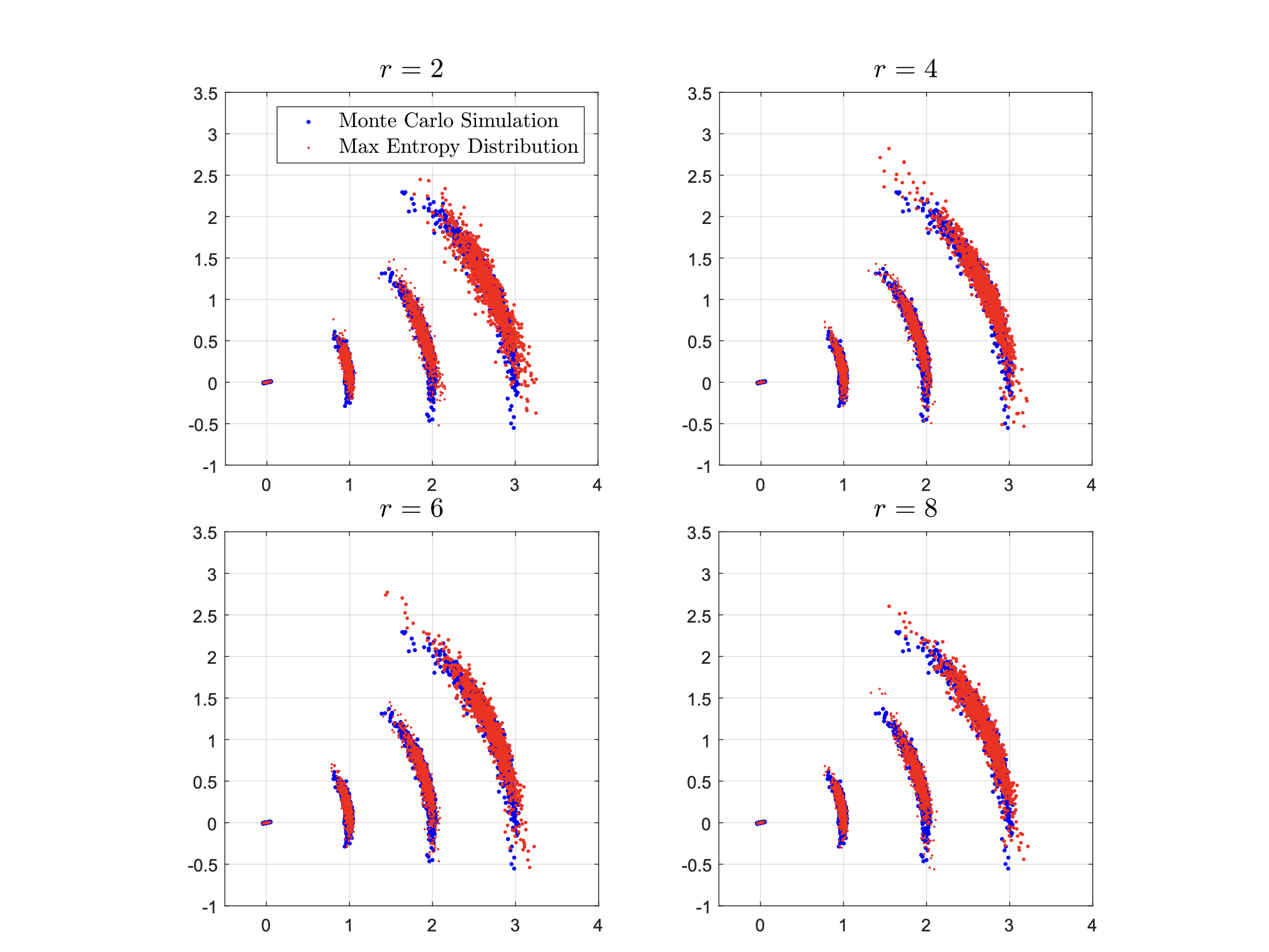
Max Entropy Moment Kalman Filter for Polynomial Systems with Arbitrary Noise
Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
We model the noise in the process and observation model of nonlinear non-Gaussian systems as Max-Entropy Distributions (MED). We propagate the moments through the process model and recover the distribution as MED, thus avoiding symbolic integration, which is generally intractable. All steps in MEM-KF, including the extraction of a point estimate, can be solved via convex optimization.
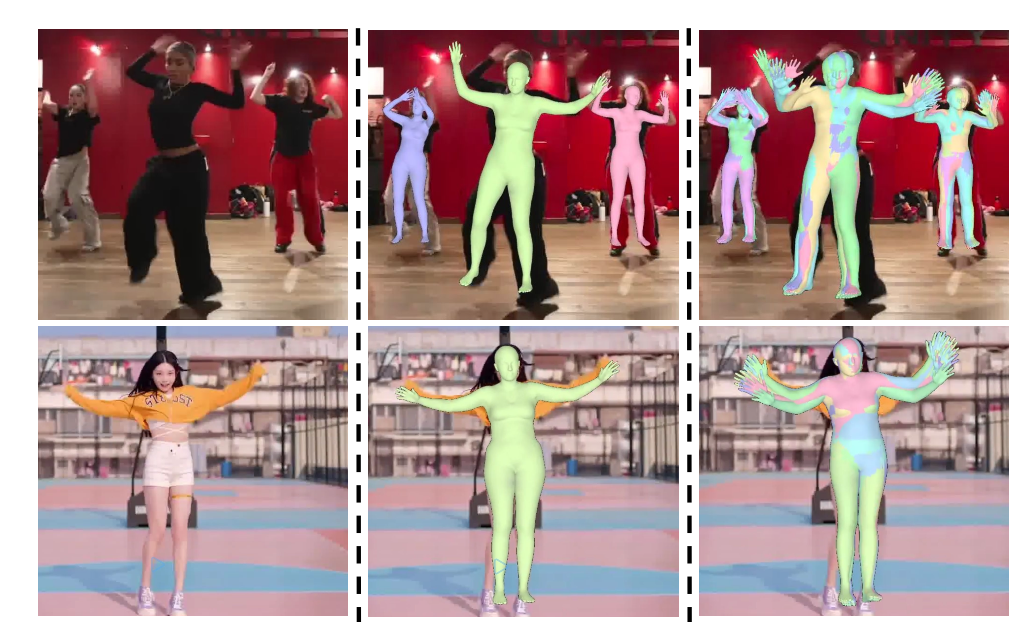

CUPS: Improving Human Pose-Shape Estimators with Conformalized Deep Uncertainty
International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025
We introduce CUPS, a novel method for learning sequence-to-sequence 3D human shapes and poses from RGB videos with uncertainty quantification. We develop a method to score multiple hypotheses proposed during training, effectively integrating uncertainty into the learning process. This results in a deep uncertainty function trained end-to-end with the 3D pose estimator.
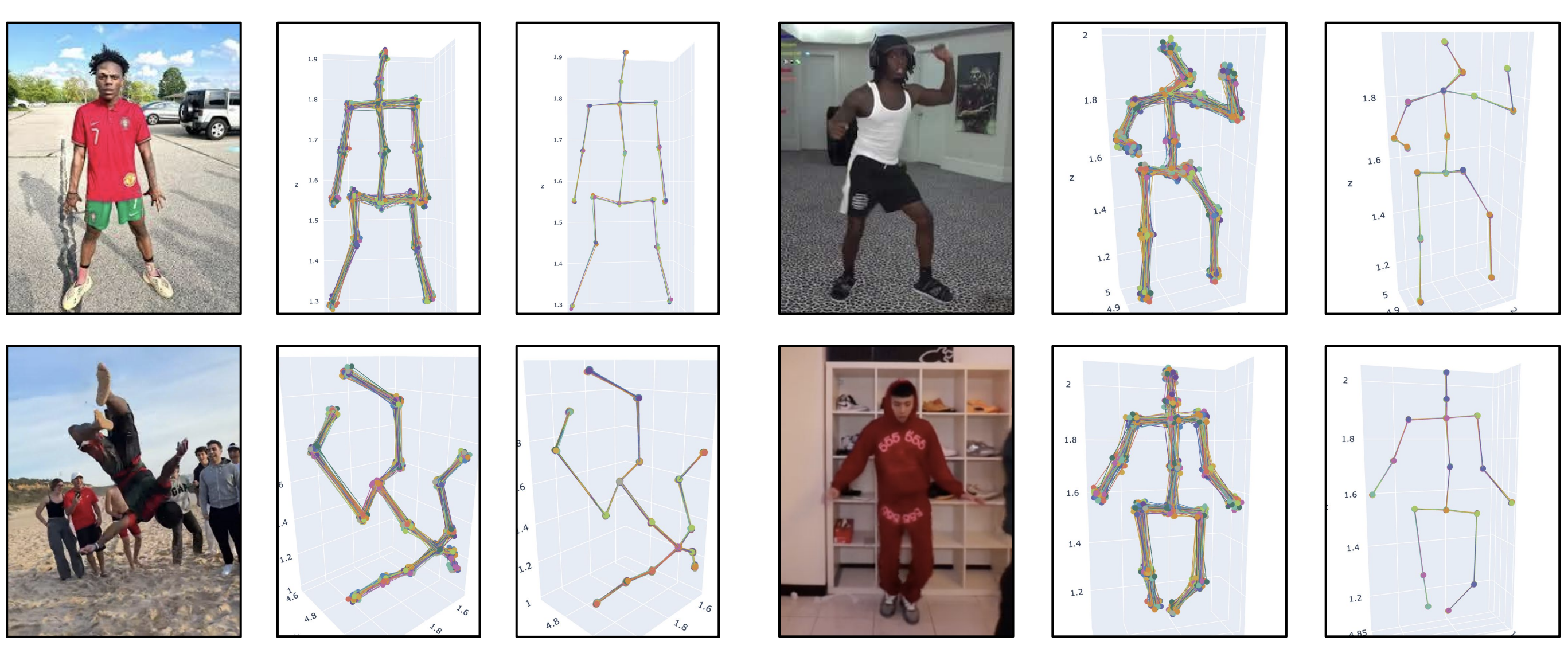

CHAMP: Conformalized 3D Human Multi-Hypothesis Pose Estimators
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2025
We introduce CHAMP, a novel method for learning sequence-to-sequence, multi-hypothesis 3D human poses from 2D keypoints by leveraging a conditional distribution with a diffusion model. We generate and aggregate multiple 3D pose hypotheses, developing a differentiable conformal predictor trained end-to-end with the 3D pose estimator.
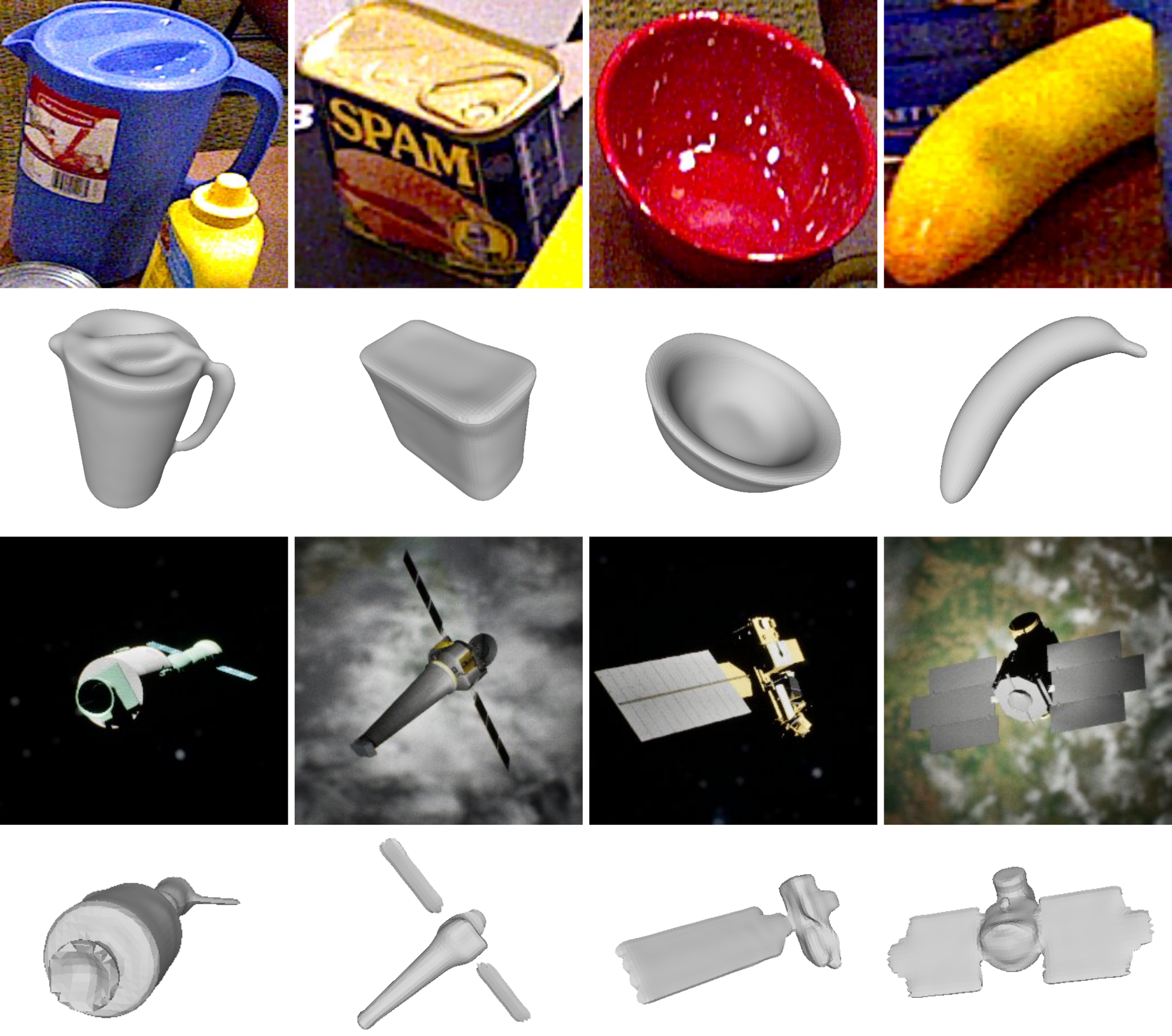

CRISP: Object Pose and Shape Estimation with Test-Time Adaptation
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025. Spotlight.
We introduce CRISP, a category-agnostic object pose and shape estimation pipeline implementing an encoder-decoder model for shape estimation. It uses FiLM-conditioning for implicit shape reconstruction and a DPT-based network for estimating pose-normalized points. We also propose an optimization-based pose and shape corrector that can correct estimation errors caused by a domain gap.

Multi-Model 3D Registration: Finding Multiple Moving Objects in Cluttered Point Clouds
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024
We investigate a variation of the 3D registration problem, named multi-model 3D registration. We are given two point clouds picturing a set of objects at different poses (and possibly including background points) and want to simultaneously reconstruct how all objects moved between the two point clouds.
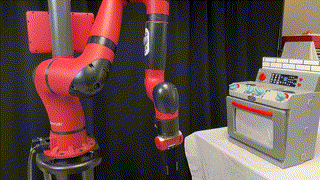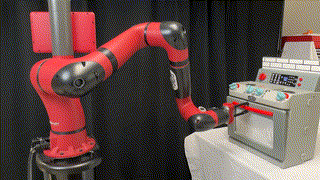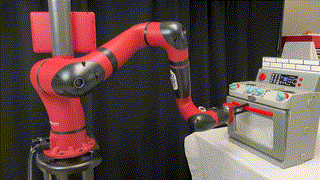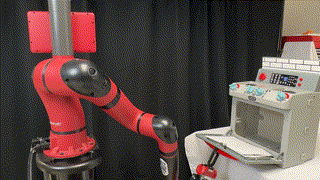
FlowBot++: Learning Generalized Articulated Objects Manipulation via Articulation Projection
Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 2023
We explore a novel method to perceive and manipulate 3D articulated objects that generalizes to enable the robot to articulate unseen classes of objects.
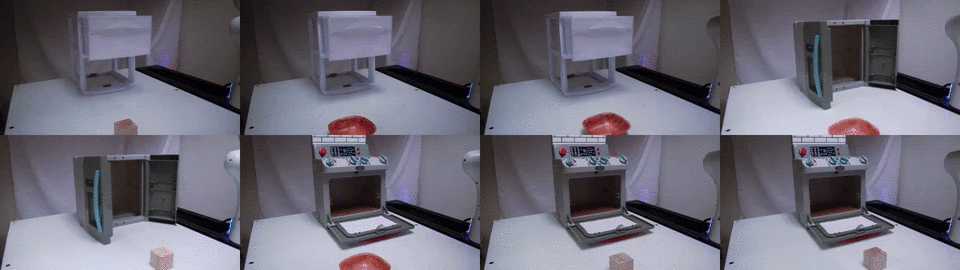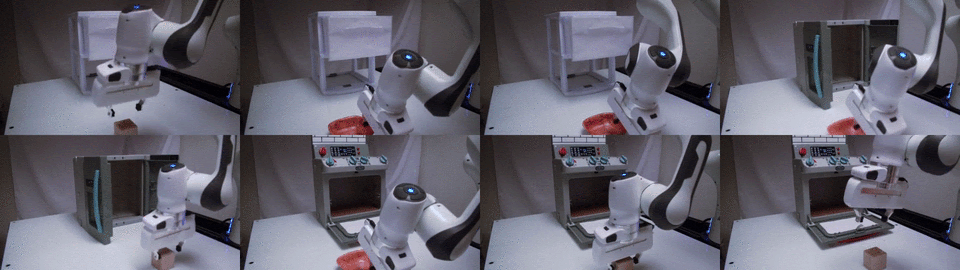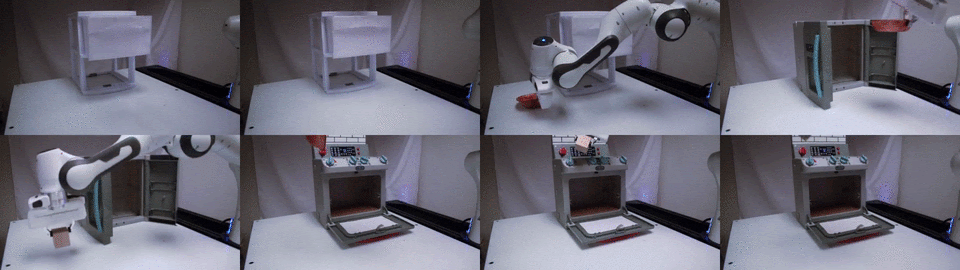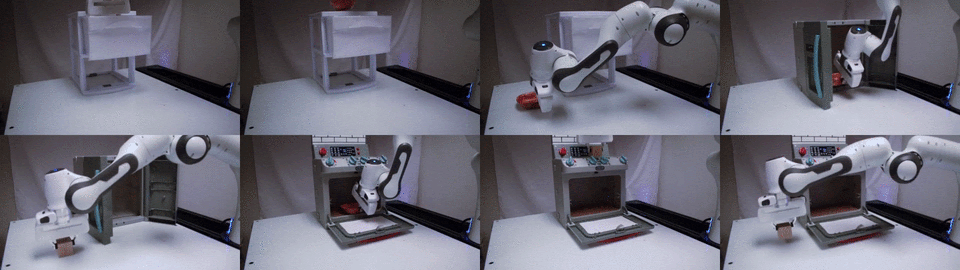
TAX-Pose: Task-Specific Cross-Pose Estimation for Robot Manipulation
Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 2022 (* indicates equal contribution)
We conjecture that the task-specific pose relationship between relevant parts of interacting objects is a generalizable notion of a manipulation task that can transfer to new objects. We propose a vision-based system that learns to estimate the cross-pose between two objects for a given manipulation task.

FlowBot3D: Learning 3D Articulation Flow to Manipulate Articulated Objects
Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2022 (* indicates equal contribution) — Long talk, Best Paper Award Finalist (Selection Rate 1.5%)
We explore a novel method to perceive and manipulate 3D articulated objects that generalizes to enable the robot to articulate unseen classes of objects.
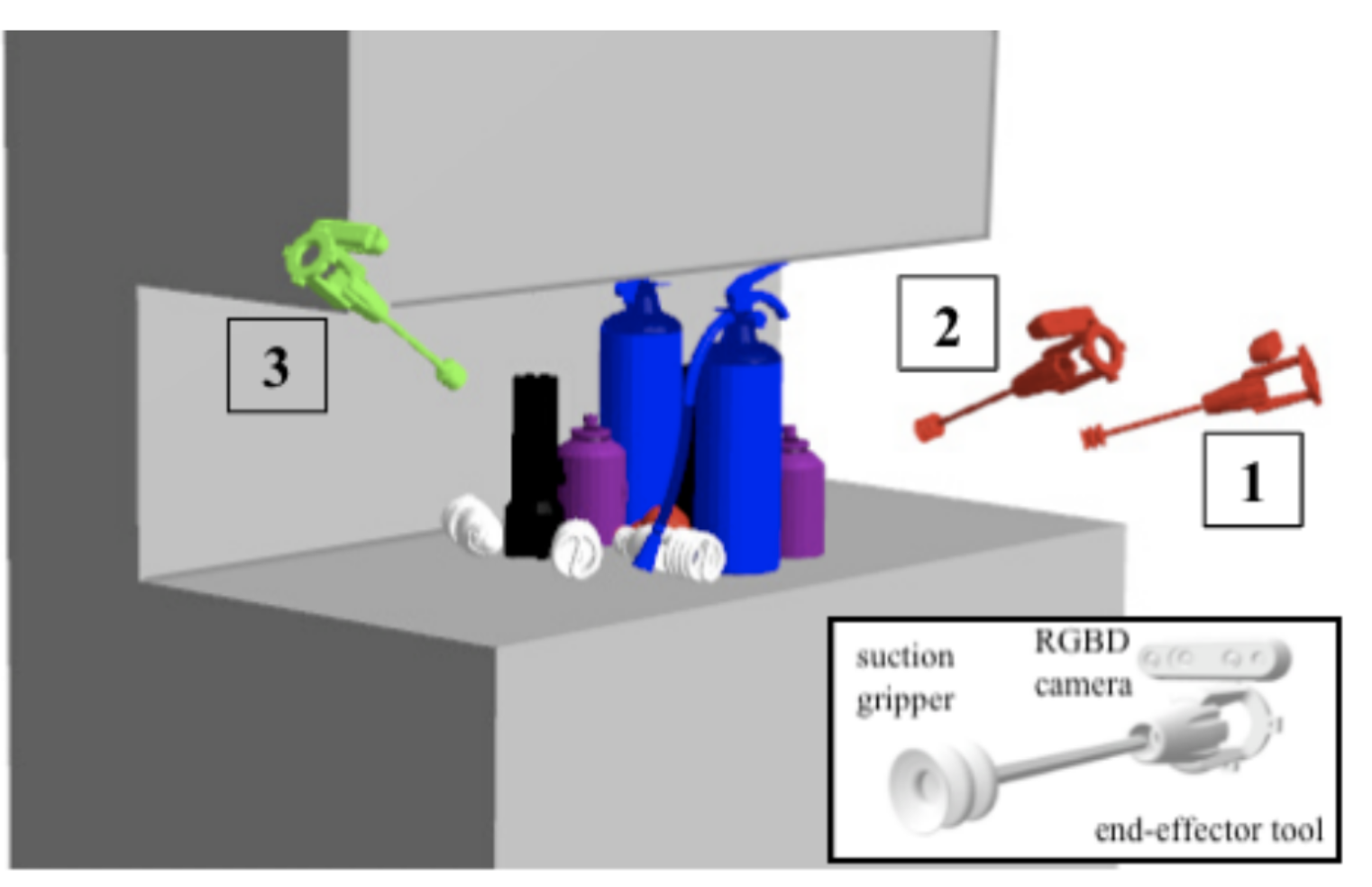
AVPLUG: Approach Vector Planning for Unicontact Grasping amid Clutter
Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2021
We present AVPLUG: Approach Vector Planning for Unicontact Grasping — an algorithm for efficiently finding the approach vector using an efficient oct-tree occupancy model and Minkowski sum computation to maximize information gain.

Robots of the Lost Arc: Self-Supervised Learning to Dynamically Manipulate Fixed-Endpoint Cables
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021
We propose a self-supervised learning framework that enables a UR5 robot to dynamically manipulate cables. The framework finds a 3D apex point for the robot arm, which, together with a task-specific trajectory function, defines an arcing motion that dynamically manipulates the cable to perform tasks with varying obstacle and target locations.
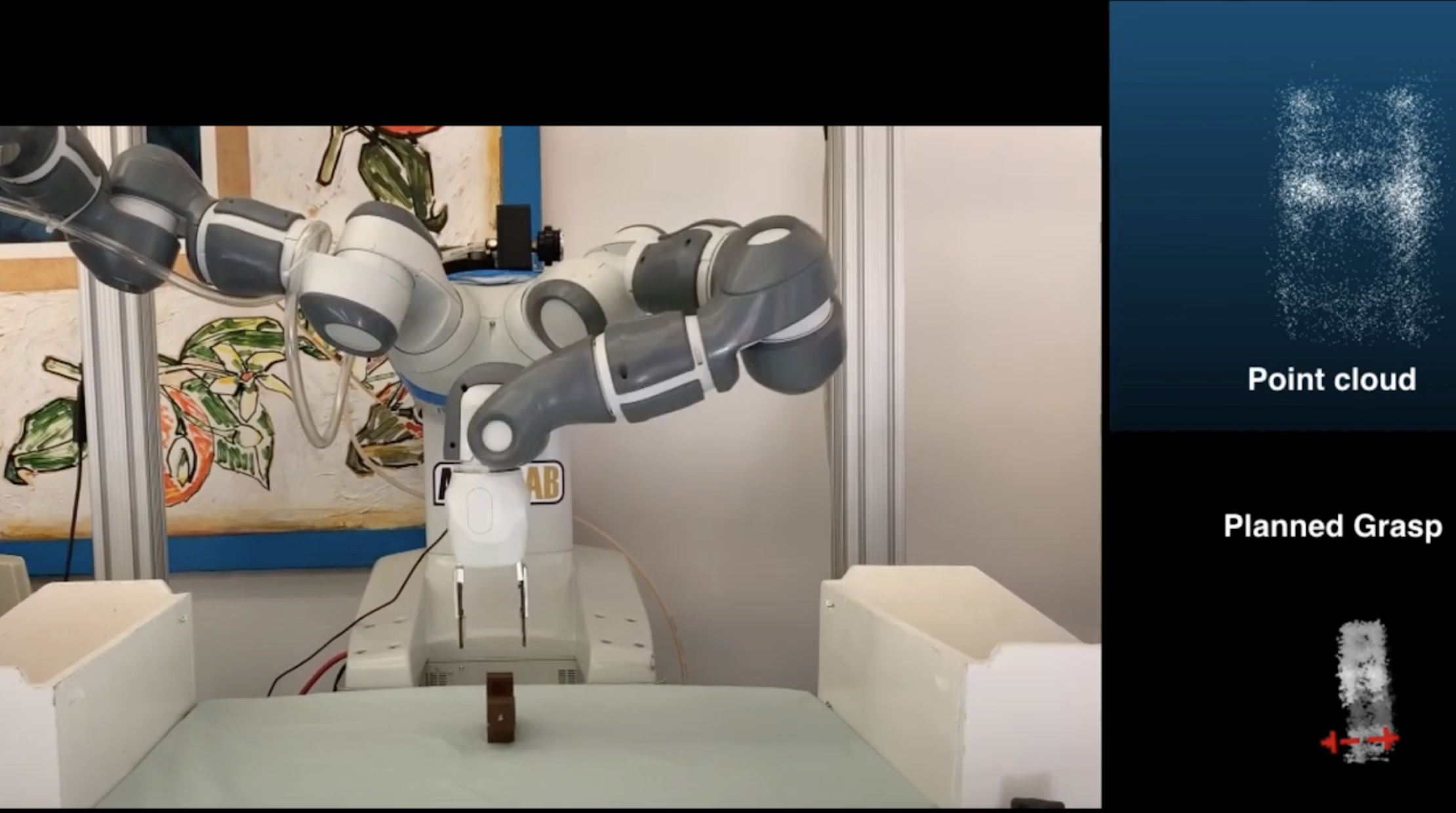

Dex-Net AR: Distributed Deep Grasp Planning Using a Commodity Cellphone and Augmented Reality App
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2020
We present Dex-Net AR, a distributed pipeline that allows point clouds to be uploaded to a server, cleaned, and evaluated by the Dex-Net grasp planner to generate a grasp axis that is returned and displayed as an overlay on the object.
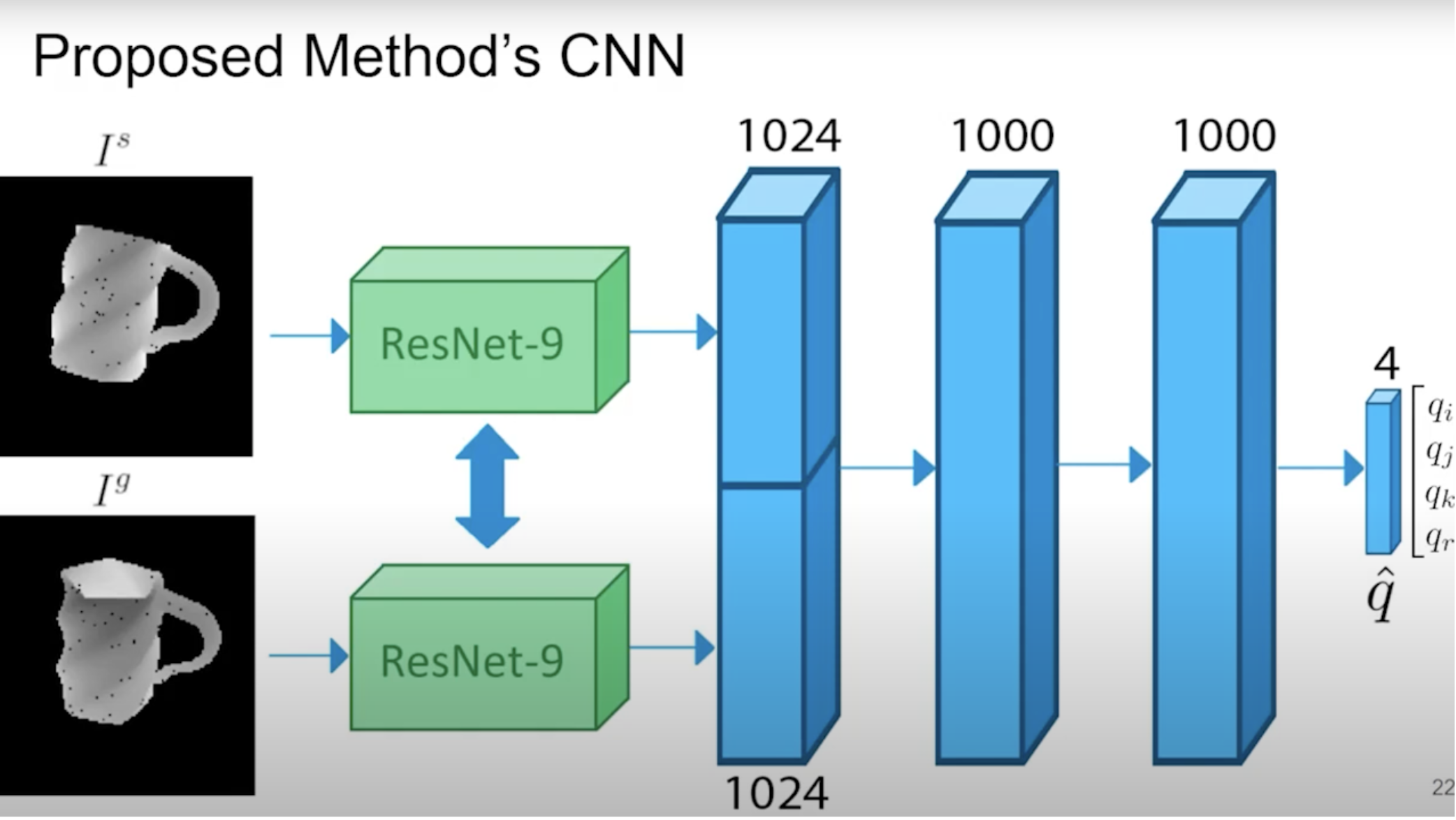
Orienting Novel Objects using Self-Supervised Rotation Estimation
Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2020
We present an algorithm to orient novel objects given a depth image of the object in its current and desired orientation.
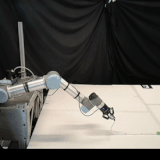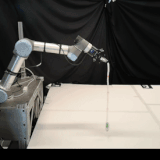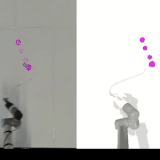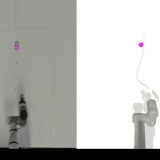
Self-Supervised Learning of Dynamic Planar Manipulation of Free-End Cables
Preprint, in submission to ICRA, 2022
We present an algorithm to train a robot to control free-end cables in a self-supervised fashion.
Safe Deep Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Lyapunov Functions
Preprint, 2022
We introduce and explore a novel method for adding safety constraints for model-based RL during training and policy learning.